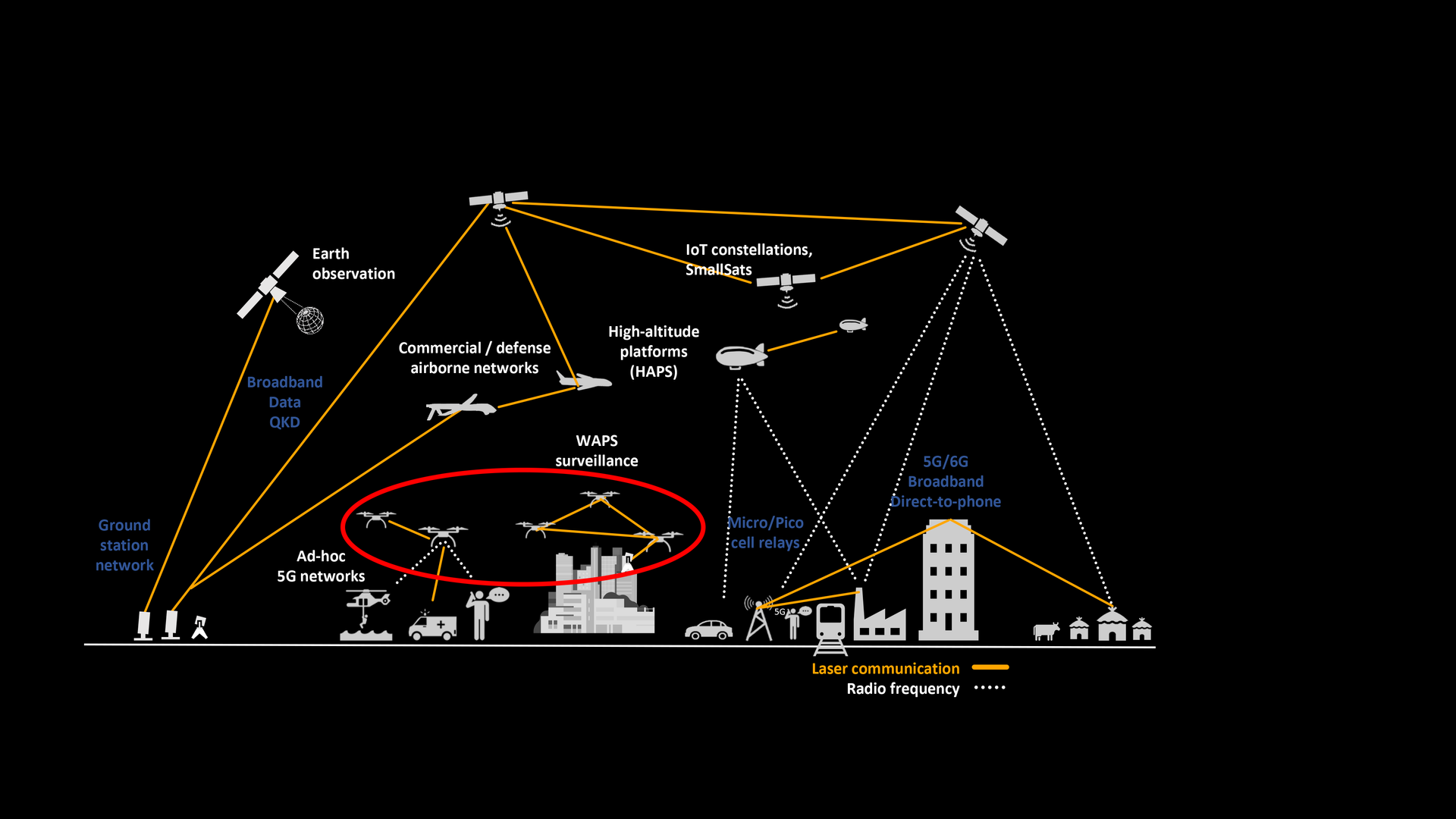
Technology
Radio Frequency vs. Laser Communication
Radio frequency (RF) communication for airborne and satellite platforms is reaching its overall limits. Bandwidth is limited due to physics itself and the restricted availability of usable frequency spectrum. Also, there are interference issues between users (e.g. satellite and cell phone infrastructure). But what is particularly critical is that licenses for the use of RF communication are highly regulated and expensive. There are also a few things to consider when it comes to secure communication: radio links can be jammed, intercepted, and spoofed.
Laser communication in fibers is well established in terrestrial networks, in many cases substituting copper since the 1990s. Today transmitting data via wireless laser connections instead of RF takes communication to the next level. It is easy and cheaper to deploy as there are no country specific ITU frequency licenses required, and it transmits larger amounts of data (>10x) in less time at affordable costs. Laser communication is inherently very robust against any kind of jamming and spoofing. In addition, a laser link is very difficult to detect, and the terminals can hardly be localized, which significantly increases the security of the operators on ground and for the flight platform. This makes laser communication the next high-rate standard in airborne communication.
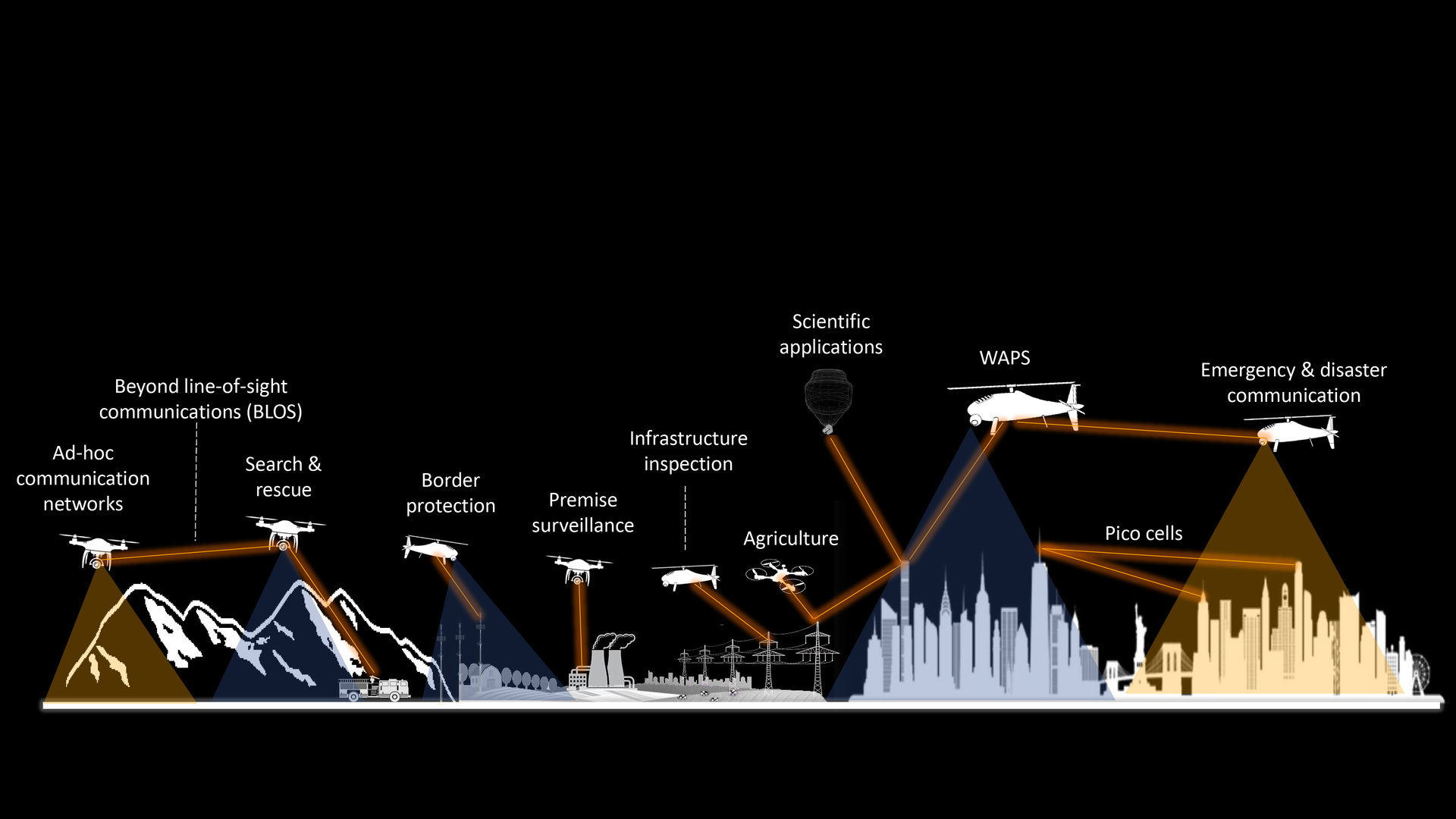
Applications for Laser Communication in Unmanned Aerial Systems (UAV/UAS)
Areas of application for laser communication include all types of data connections that are still realized with radio today. Laser communication is particularly suitable for unmanned aerial systems, which transmit large amounts of data from on-board sensors and require resilient communication. The UAV market has emerged and grown over the last 20 years. With millions of UAVs widely used in many countries, licensing of spectrum, organized by each country individually, becomes an issue. This creates significant effort in operating UAVs in different countries.
Laser communication enables new ways of communication. Applications can be found in remote sensing, ad-hoc mobile communication networks (e.g. in disaster zones), search & rescue operations, surveillance scenarios (wide area persistent surveillance, infrastructure), inspection and surveying in energy and environment, high-bandwidth communication for sport events and filming industry, reliable communication for security and many more.